GDPR & Data Protection Governance: Built for ISO27001 & SOC 2 Compliance

“Secure Today, Confident Tomorrow”
In an era of heightened economic uncertainty and rapid social change, Zebsoft understands that the security of your information is paramount. Our unwavering commitment to data protection is reflected in our adherence to the highest industry standards and certifications.
Why Choose Zebsoft for Information Security?
- Certified Excellence: Zebsoft is proud to be aligned with top-tier information security standards, including ISO/IEC 27001 and SOC 2, ensuring your data is safeguarded by the best practices in the industry.
- Compliance and Beyond: We not only provide controls for global data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA but also go above and beyond to exceed these standards, offering you unparalleled security and compliance.
- Risk Mitigation: Our advanced security measures are designed to enable you to protect your valuable data from cyber threats and breaches, minimising risks and securing your digital assets.
- Customer-Centric Security: At Zebsoft, we prioritize your peace of mind. Our transparent and robust data handling and protection protocols ensure that you can focus on your business with confidence.
Join Zebsoft, where your information security is our mission. Together, we can navigate today’s challenges with confidence and build a secure tomorrow.
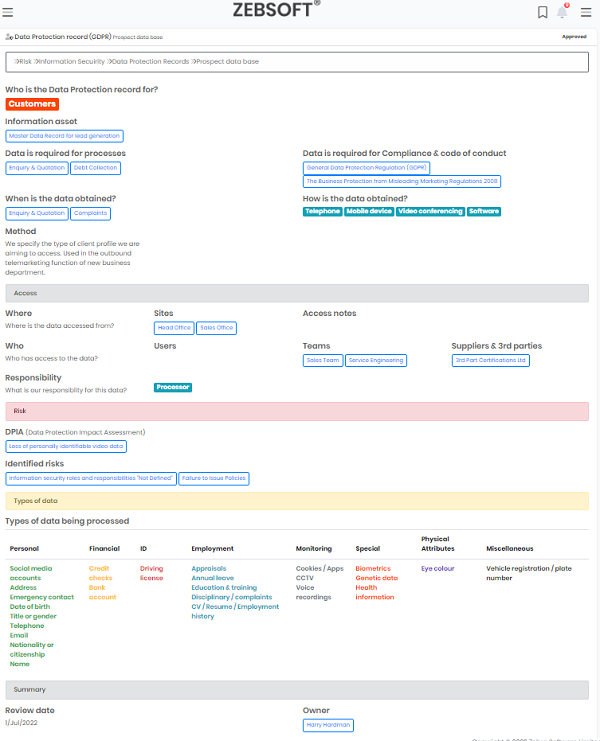
Maintaining accurate Information security records
The crucial aspect to making sure you Information security software and GPDR is followed. The majority of businesses and organisations also require it. This has already been made mandatory in certain EU nations, but not in many others. We will provide you an outline of your responsibilities and legal requirements under the GDPR..
Your Information security software system will ensure you doing everything correctly, including record keeping, many firms may experience a great deal of stress when the GDPR is an issue to be dealt with in a formal process.
How an IMS Software System Processes Activity Records
Our Information security software will ensure that GDPR’s Article 30 is addressed in respect of record-keeping. This is one of the GDPR clauses where there is little to no ambiguity. All the provisions and requirements are clearly identified. In addition to meeting all regulatory requirements, Information security software record-keeping will provide you a better understanding of how and why the data is being used.
Comprehensive Recordkeeping by using Information security software
lot of record-keeping that must be done to achieve compliance and this is where Information security software comes into it’s own. DPA’s used by different countries have differing requirements, for instance Belgium, only the party performing the processing needs to preserve records as long as they can swiftly produce them upon request. The other parties are not required to do so. Information security software will make this kind of anomaly easy to handle ensuring you don’t step out of line.
Information security software is used to maintain records and is crucial for proving compliance with the GDPR. Without exception. When organisations must deliver these records to the supervisory authority upon request the Information security software makes this simple.
Both written and digital records must be maintained. By using Information security software your company will deploy consolidated record storage, using a cloud based database in place of Excel spreadsheets. Information security software records are not nation-specific. When a nation requests that extra information it is recorded. Contrary to the current situation, when disclosure of records is occasionally made public, the GDPR emphasises that records are internal documents, and businesses are not required to make them publicly available.
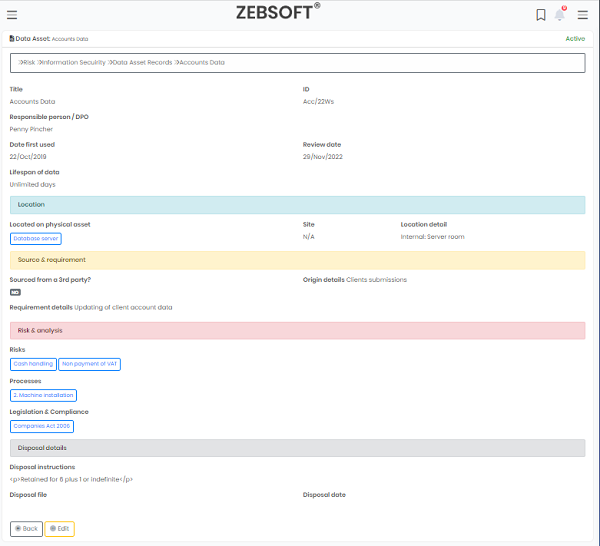
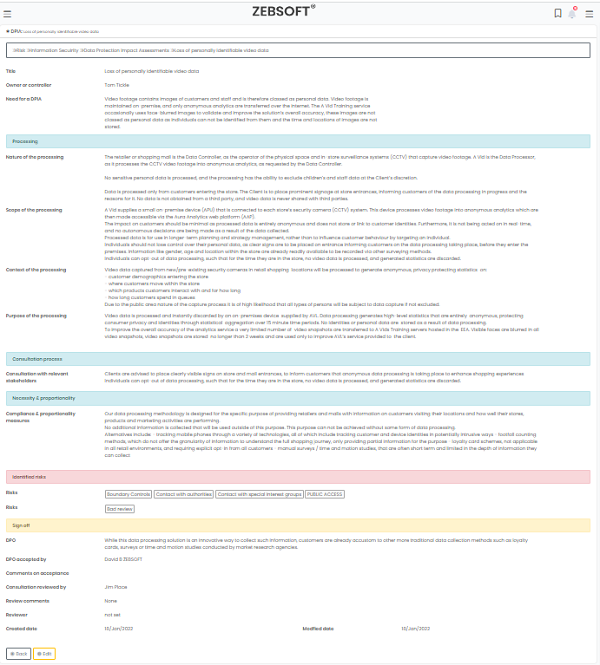
How Information security software is used to create Data Protection Impact Assessments.
You can identify and reduce a project’s data protection risks by creating a data protection impact assessment (DPIA) in your Information security software system. Where processing poses a significant risk to people, a DPIA is required. This contains a few particular categories of processing. ZEBSOFT checklists can used for screening and will assist you in determining when to conduct a DPIA.
A DPIA should be conducted for any other significant project involving the handling of personal data. The DPIA must include a description of the type, scope, context, and purposes of the processing; an evaluation of necessity, proportionality, and compliance measures; identification and evaluation of risks to individuals; and identification of any further mitigation strategies. This is all templated for you in the Information security software. Which takes into account both the likelihood and the severity of any potential effects on individuals when determining the level of risk. High risk can be caused by either a high likelihood of some harm or a low likelihood of serious injury.
Recording & measuring the results of monitoring activities:
- Formalised and consistent monitoring
- Build checklist routines
- Set alert levels
- Create tasks for individuals or teams
- Recurring individual or team tasks
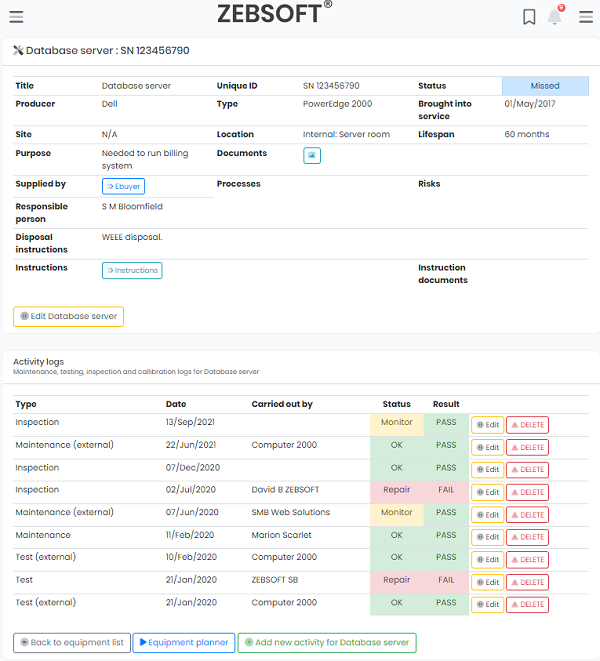
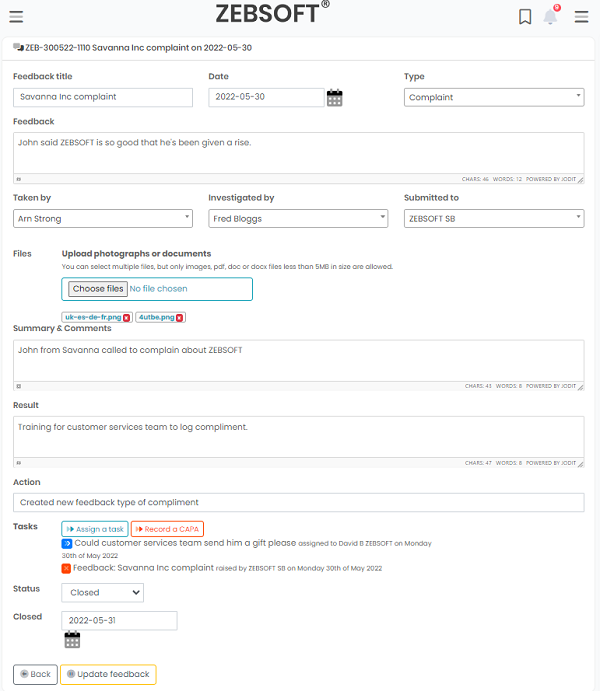
Raise & Investigate incidents:
- Planning of InfoSec activities
- Organisation wide feedback
- Control, monitor and act on feedback
- Raise non-conformance
- Record Corrective and Preventative actions
- Create comprehensive auditing programme
InfoSec Controls:
- Uncompromised recoding of events
- Easily manage your Statement of Applicability
- Easy to follow layout
- Attach identified risks to the controls

Policy Communication:
- Communication of policies
- Ensure policies are read
- Control who can see what policies
- Policy version control
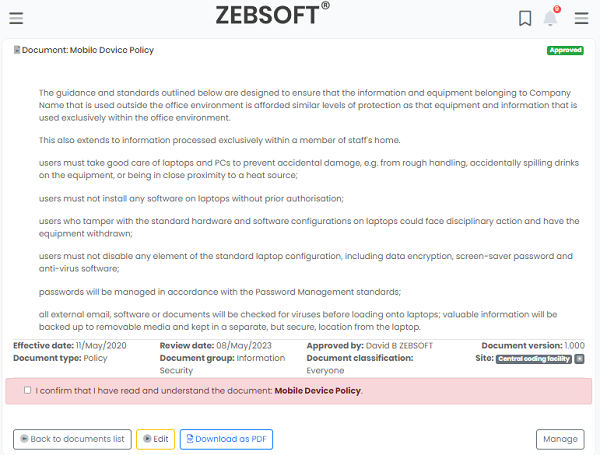
Document Issue, authority & signing:
- Record issue dates & expiry dates
- Approve documents
- Categorise and groups documents
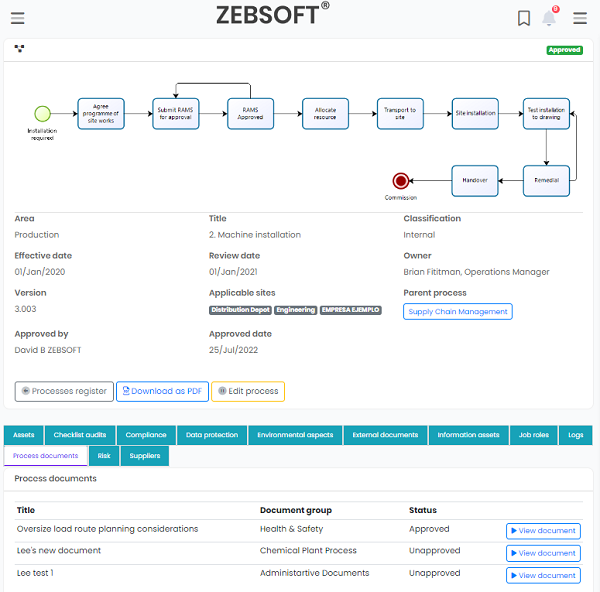
Process and protocol definition:
- See your process and communicate it effectively
- Link all important aspects directly
- Access documents directly
- Complete 360 degree visibility of controls
See the effect poor data security can have on your business bank balance:
InfoSec controls that form part of normal daily activity for all
Controlling documentation in the electronic landscape is a complex problem, we give the controls you need to ensure that everyone is using the the correct version and has access the documents they need without seeing the documents they are allowed to see.
Implementing an effective audit management system is crucial for organizations aiming to streamline their audit processes, ensure compliance, and enhance operational efficiency. ZEBSOFT’s audit management capabilities offer a comprehensive solution that empowers organisations to manage their audits seamlessly and effectively.
Here are several key reasons why implementing ZEBSOFT’s audit management system is essential:
1. Comprehensive Audit Management: ZEBSOFT’s platform provides a holistic approach to audit management, covering all stages from planning and execution to reporting and follow-up. It enables organisations to conduct various types of audits, including internal, external, compliance, and risk-based audits. This comprehensive functionality ensures that all audit requirements are met systematically, enhancing overall audit quality and efficiency.
2. Streamlined Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: In an environment of ever-increasing regulatory requirements, ZEBSOFT’s audit management system helps organisations stay compliant with industry standards and regulations. The platform supports adherence to regulations such as ISO 27001, GDPR, and other industry-specific standards. By automating compliance checks and audit trails, organisations can easily demonstrate their compliance efforts to regulators and stakeholders.
3. Effective Risk Management: ZEBSOFT’s audit management capabilities are designed to integrate risk management into the audit process. The platform allows organisations to identify, assess, and prioritise risks, ensuring that audit resources are focused on the most critical areas. By embedding risk management principles, ZEBSOFT helps organisations proactively address vulnerabilities and mitigate risks effectively.
4. Enhanced Stakeholder Trust and Transparency: A robust audit management system enhances transparency and accountability within an organisation. ZEBSOFT’s platform provides detailed and real-time insights into audit activities, findings, and corrective actions. This transparency builds stakeholder trust and confidence, demonstrating the organisation’s commitment to maintaining high standards of governance and operational integrity.
5. Improved Operational Efficiency: ZEBSOFT’s audit management system automates and streamlines the audit process, reducing the administrative burden on audit teams. Features such as automated scheduling, notifications, and workflow management help ensure that audits are conducted efficiently and on time. This improved efficiency allows audit teams to focus on strategic analysis and value-added activities rather than repetitive administrative tasks.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making: ZEBSOFT’s platform provides advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling organisations to gain actionable insights from their audit data. By leveraging data-driven insights, organisations can make informed decisions to enhance their processes, improve compliance, and strengthen their overall risk posture. Customised dashboards and reports ensure that key information is easily accessible to decision-makers.
7. Continuous Improvement and Adaptability: ZEBSOFT promotes a culture of continuous improvement by enabling organisations to monitor and review their audit processes regularly. The platform supports ongoing assessment and refinement of audit practices, ensuring that they evolve in response to changing risks and regulatory requirements. This adaptability helps organisations stay ahead of emerging threats and maintain a robust audit framework.
8. Seamless Integration with Existing Systems: ZEBSOFT’s audit management system is designed to integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems, such as ERP, CRM, and risk management platforms. This interoperability ensures that audit data is consistent, accurate, and up-to-date across the organization. The ability to integrate with existing systems also reduces implementation time and enhances the overall user experience.
In summary, implementing ZEBSOFT’s audit management system is essential for organisations looking to streamline their audit processes, ensure compliance, manage risks effectively, enhance stakeholder trust, and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging ZEBSOFT’s comprehensive and adaptable platform, organisations can achieve a robust and efficient audit management framework that supports their strategic objectives.
Implementing a management system for data protection and compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is of utmost importance for organizations that handle personal data.
Here are several key reasons why the ZEBSOFT GRC Platform is used to addresses management system requirements:
1. Legal Compliance: The GDPR sets strict guidelines for the processing, storage, and protection of personal data. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines, legal actions, and reputational damage. By implementing a management system for data protection and GDPR, organizations can ensure they meet the regulatory requirements, maintain compliance, and mitigate the risk of legal consequences.
2. Data Security: Data breaches and unauthorized access to personal information can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations. Implementing a management system helps establish appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, loss, alteration, or destruction. It includes policies, procedures, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring data security.
3. Risk Management: Implementing a management system for data protection and GDPR involves conducting risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to personal data. Organizations can then implement controls and measures to mitigate those risks effectively. By systematically managing risks associated with personal data processing, organizations can minimize the likelihood of data breaches, reputation damage, and regulatory penalties.
4. Enhanced Customer Trust: Data protection and GDPR compliance contribute to building and maintaining customer trust. When customers entrust their personal information to an organization, they expect that it will be handled with care and in compliance with privacy regulations. Implementing a management system for data protection and GDPR demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding personal data, which enhances customer trust, strengthens relationships, and increases customer loyalty.
5. Improved Data Governance: A management system provides a framework for establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and processes related to data protection and GDPR compliance. It helps organizations define and implement data governance policies, data inventory and mapping, data protection impact assessments, and data subject rights management. These measures enhance transparency, accountability, and the overall governance of personal data within the organization.
6. Privacy by Design and Default: GDPR emphasizes the principle of “privacy by design and default,” which requires organizations to consider data protection and privacy from the inception of any system or process that involves personal data. Implementing a management system helps embed privacy considerations into the organization’s practices, policies, and technical infrastructure. It ensures that privacy is integrated into the design, development, and implementation of systems and processes, reducing the risk of non-compliance and privacy breaches.
7. Data Subject Rights Management: GDPR grants individuals certain rights regarding their personal data, including the right to access, rectify, erase, and restrict processing of their data. Implementing a management system helps organizations establish processes and procedures for handling data subject requests effectively. It ensures that requests are acknowledged, processed, and responded to within the required timeframes, enabling organizations to meet their obligations and maintain compliance with data subject rights.
8. Continuous Improvement: A management system for data protection and GDPR provides a foundation for ongoing improvement and refinement of data protection practices. It enables organizations to monitor their compliance status, conduct regular audits and assessments, identify areas for improvement, and implement corrective actions. By continually enhancing data protection measures, organizations can adapt to evolving threats, technologies, and regulatory requirements, ensuring ongoing compliance and data security.
In summary, implementing a management system for data protection and GDPR is crucial for organizations to achieve legal compliance, protect personal data, manage risks, build customer trust, improve data governance, incorporate privacy by design, effectively manage data subject rights, and drive continuous improvement. By prioritizing data protection and GDPR compliance, organizations can protect the rights and privacy of individuals and maintain a strong and trusted reputation.
Implementing a management system for Service Organization Control 2 (SOC 2) compliance is important for organizations that provide services involving the processing, storage, and transmission of customer data. SOC 2 is a widely recognized standard for evaluating and reporting on the controls in place for data security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Here are several key reasons why implementing the ZEBSOFT GRC Platform to addresses SOC 2 is crucial:
1. Trust and Assurance: SOC 2 compliance provides customers and stakeholders with assurance that an organization has implemented effective controls to protect their data. By implementing a management system aligned with SOC 2 requirements, organizations demonstrate a commitment to data security, privacy, and the integrity of their services. This fosters trust, differentiates them in the market, and enhances their reputation.
2. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Many industries have regulatory requirements related to the security and privacy of customer data. Implementing a management system for SOC 2 helps organizations meet these requirements by establishing appropriate controls and processes. SOC 2 compliance can help organizations demonstrate compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) or the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in the United States.
3. Risk Management: Implementing a management system for SOC 2 involves conducting risk assessments and implementing controls to mitigate identified risks. This helps organizations identify vulnerabilities and threats to the security, availability, and integrity of customer data. By effectively managing risks, organizations can prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, system failures, and other security incidents that could result in financial losses, legal consequences, and reputational damage.
4. Competitive Advantage: SOC 2 compliance can provide a competitive advantage in industries where data security and privacy are critical factors. By demonstrating SOC 2 compliance, organizations signal their commitment to protecting customer data and differentiate themselves from competitors who may not have achieved similar levels of assurance. This can be a deciding factor for customers when choosing service providers, especially in industries such as cloud computing, technology, finance, and healthcare.
5. Third-Party Assurance: SOC 2 compliance often involves an independent audit or assessment by a qualified third party. This provides an additional layer of assurance to customers and stakeholders that the organization’s controls have been independently evaluated. The audit report can be shared with customers, partners, and regulators as evidence of compliance, streamlining the due diligence process and building confidence in the organization’s security practices.
6. Internal Process Improvement: Implementing a management system for SOC 2 requires organizations to establish and document policies, procedures, and controls to meet SOC 2 requirements. This process helps organizations identify areas for improvement, enhance internal processes, and align their operations with industry best practices. By continually assessing and refining controls, organizations can improve the security and efficiency of their operations.
7. Vendor Management: SOC 2 compliance is often required by organizations when selecting third-party service providers. By implementing a management system for SOC 2, organizations can provide the necessary assurance to their customers that they have implemented adequate controls to protect customer data. This facilitates vendor management processes and strengthens relationships with customers who prioritize data security and privacy.
8. Data Protection and Privacy: SOC 2 compliance requires organizations to establish controls and processes to protect the confidentiality and privacy of customer data. By implementing a management system, organizations can ensure that appropriate measures are in place to safeguard sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and comply with applicable data protection regulations. This helps organizations meet customer expectations for data security and privacy.
In summary, implementing a management system for SOC 2 compliance is important for organizations to build trust, meet regulatory requirements, manage risks, gain a competitive advantage, provide third-party assurance, improve internal processes, facilitate vendor management, and protect customer data. SOC 2 compliance demonstrates a commitment to the security, availability, processing integrity
Implementing an ISO 27001 Information Security Management System (ISMS) is important for organizations that aim to establish a robust framework for managing and protecting their information assets. ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks.
Here are several key reasons why implementing the ZEBSOFT GRC Platform for ISMS is crucial:
1. Comprehensive Information Security: ISO 27001 helps organizations establish a holistic approach to information security. It covers various aspects, including confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. By implementing an ISMS, organizations can identify and assess information security risks, implement appropriate controls, and manage these risks effectively. This ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, reducing the likelihood of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents.
2. Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Information security regulations and requirements are becoming increasingly stringent across different industries and jurisdictions. ISO 27001 provides a framework that helps organizations meet these legal and regulatory obligations. Implementing an ISMS ensures that organizations have appropriate controls and processes in place to protect sensitive information and comply with applicable laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other data protection regulations.
3. Risk Management: ISO 27001 focuses on risk management principles and processes. By implementing an ISMS, organizations can conduct systematic risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to their information assets. This allows them to implement appropriate controls and countermeasures to mitigate these risks effectively. Through continuous monitoring and improvement, organizations can proactively manage information security risks and protect their critical assets.
4. Enhanced Customer Trust and Reputation: Information security breaches can lead to significant reputational damage and loss of customer trust. Implementing an ISO 27001 ISMS provides a clear demonstration of an organization’s commitment to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of customer data. It reassures customers and stakeholders that their information is managed and protected in accordance with internationally recognized best practices. This helps build trust, enhances the organization’s reputation, and can give it a competitive edge.
5. Improved Business Opportunities: Many organizations now require their vendors and partners to demonstrate strong information security practices. Implementing an ISO 27001 ISMS can provide a competitive advantage by meeting the expectations of potential customers and partners. It can serve as a differentiating factor during procurement processes, demonstrating that the organization has implemented appropriate controls and measures to safeguard sensitive information. This opens up new business opportunities and strengthens existing relationships.
6. Incident Response and Business Continuity: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of incident response planning and business continuity management. Implementing an ISMS helps organizations establish procedures and processes to effectively respond to and recover from information security incidents. This ensures a timely and efficient response, minimizes the impact of incidents, and helps maintain business continuity.
7. Continuous Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continuous improvement in information security. By implementing an ISMS, organizations establish a framework for ongoing monitoring, measurement, and improvement of their information security practices. Regular audits, management reviews, and assessments help identify areas for improvement, allowing organizations to enhance their security posture and adapt to evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
8. Supply Chain Management: Information security is a critical consideration in supply chain management. Organizations often need to assess the information security practices of their suppliers and partners. Implementing an ISO 27001 ISMS provides a standardized framework for evaluating the security capabilities of third parties. It enables organizations to assess supplier risks, define security requirements, and ensure that their supply chain partners meet the necessary information security standards.
In summary, implementing an ISO 27001 Information Security Management System is important for organizations to establish comprehensive information security, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, manage risks effectively, build customer trust and reputation, unlock business opportunities, ensure incident response and business continuity
The ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability (SoA) is a key document within the Information Security Management System (ISMS) framework. It provides a summary of the organization’s approach to information security and specifies the scope of the ISMS.
ZEBSOFT GRC Platform Statement of Applicability:
1. Scope Definition: The SoA begins with a clear definition of the scope of the ISMS. This defines the boundaries within which the organization intends to implement information security controls. It specifies the departments, systems, processes, and locations that are included in the scope and identifies any specific exclusions.
2. Identification of Control Objectives and Controls: The SoA identifies the control objectives and controls that are applicable to the organization. Control objectives are the goals or outcomes that the organization seeks to achieve through the implementation of controls. Controls, on the other hand, are specific measures or safeguards that are implemented to address information security risks.
3. Control Applicability Assessment: For each control objective and control identified, the organization assesses its applicability. This assessment determines whether the control is relevant and necessary based on the organization’s risk assessment, legal and regulatory requirements, and business objectives. Controls that are deemed not applicable are excluded from the SoA.
4. Control Implementation Status: The SoA indicates the status of control implementation. This includes specifying whether the control is already implemented, partially implemented, or planned for future implementation. It helps in tracking the progress of control implementation and provides transparency on the organization’s information security maturity.
5. Justification for Exclusions: If any controls or control objectives are excluded from the scope, the SoA provides a justification for their exclusion. This explanation should be based on a risk assessment and should consider factors such as cost-effectiveness, technical feasibility, and the organization’s risk appetite. The justification ensures transparency and accountability for the decision to exclude specific controls.
6. Supporting Documentation: The SoA references supporting documentation that provides evidence and further details regarding the implementation of controls. This can include policies, procedures, guidelines, standards, or other relevant documents that demonstrate how the organization is meeting the control objectives.
7. Review and Approval: The SoA is a formal document that requires review and approval by management. This ensures that the identified controls and their applicability align with the organization’s overall objectives and that the document accurately reflects the organization’s information security posture.
8. Ongoing Updates: The SoA is a living document that should be reviewed and updated regularly. As the organization evolves, changes its information systems, or faces new risks, the SoA should be revised accordingly. It ensures that the scope and applicability of controls remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s changing information security requirements.
The ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability plays a crucial role in documenting the organization’s information security control framework. It provides a clear understanding of the scope of the ISMS, the identified control objectives and controls, their applicability, and their implementation status. The SoA is an essential reference document during internal and external audits, demonstrating the organization’s commitment to information security and compliance with ISO 27001 requirements.
ZEBSOFT GRC Platform policies management:
1. Policy Development: The first step is to develop information security policies that align with the organization’s objectives, legal and regulatory requirements, and industry best practices. These policies define the organization’s overall approach to information security and provide a high-level framework for protecting information assets.
2. Policy Framework: The organization establishes a policy framework that outlines the structure and content of the information security policies. This framework typically includes a policy hierarchy, where higher-level policies provide overarching direction, while lower-level policies provide more detailed guidance on specific areas of information security.
3. Policy Customization: Organizations need to customize the policies to suit their specific business environment, risks, and operational requirements. This involves tailoring the policies to address the organization’s unique information security challenges and aligning them with the organization’s culture and practices.
4. Policy Implementation: Once the policies are developed and customized, they are communicated to all relevant stakeholders within the organization. This includes employees, contractors, and any other individuals who have access to or are involved in the handling of sensitive information. Training and awareness programs may be conducted to ensure that employees understand the policies and their responsibilities.
5. Policy Adoption: Employees are required to acknowledge their understanding and adherence to the information security policies. This acknowledgment can be obtained through signed agreements, acceptance forms, or other formal mechanisms. It ensures that employees are aware of the policies and agree to comply with them.
6. Policy Maintenance: Information security policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the business environment, technology, regulations, and emerging threats. A policy review and maintenance process should be established to ensure that the policies remain relevant and effective. This may involve conducting periodic policy audits, seeking input from stakeholders, and aligning the policies with changes in the organization’s risk landscape.
7. Policy Enforcement: Organizations need to establish mechanisms for enforcing the information security policies. This may include implementing procedures, guidelines, and technical controls that support the policies’ implementation. Regular monitoring, audits, and assessments can help ensure that employees and systems adhere to the policies, and corrective actions can be taken if policy violations are identified.
8. Policy Communication and Awareness: Ongoing communication and awareness programs are essential to ensure that employees remain informed and educated about the information security policies. This may involve regular training sessions, newsletters, internal communications, and reminders to reinforce the importance of compliance with the policies.
9. Policy Documentation: Information security policies should be properly documented and maintained in a central repository or policy management system. This ensures that the policies are easily accessible, up-to-date, and can be referenced by employees, auditors, and other stakeholders as needed.
10. Policy Governance: Effective policy governance involves assigning responsibility for the management and oversight of the information security policies. This may include designating a policy owner or a policy management team who are responsible for policy development, updates, communication, and enforcement.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively manage their ISO 27001 policies, ensuring that they remain relevant, communicated, and enforced throughout the organization. This contributes to the establishment of a strong information security culture and supports the organization in protecting its valuable information assets.
ZEBSOFT GRC Platform data asset management:
1. Asset Inventory: ISO 27001 emphasizes the need for organizations to identify and maintain an inventory of information assets, which includes data assets. This involves identifying and documenting the types of data assets that the organization handles, such as customer data, financial data, intellectual property, or any other critical data.
2. Asset Classification: ISO 27001 encourages organizations to classify their information assets based on their value, sensitivity, and criticality. This classification helps in prioritizing security controls and determining appropriate protection measures for different data assets. The classification may consider factors such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability requirements.
3. Risk Assessment: ISO 27001 requires organizations to conduct a systematic risk assessment process to identify and assess risks to their information assets, including data assets. This involves analyzing threats and vulnerabilities that may impact the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. The risk assessment helps prioritize the allocation of resources for implementing security controls.
4. Controls Implementation: ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive set of controls in Annex A, which can be applied to protect information assets, including data assets. These controls cover various aspects such as access control, encryption, backup and recovery, incident management, and more. Organizations should select and implement controls based on their risk assessment and the specific requirements of their data assets.
5. Data Protection Measures: ISO 27001 requires organizations to establish and implement appropriate measures to protect data assets. This includes implementing access controls to restrict unauthorized access, encryption to safeguard data during storage and transmission, backup and recovery procedures to ensure data availability, and measures to detect and respond to security incidents affecting data assets.
6. Data Retention and Disposal: ISO 27001 emphasizes the need for organizations to define data retention and disposal policies. These policies determine how long data assets should be retained based on legal, regulatory, contractual, or business requirements. When data assets are no longer required, organizations should have procedures in place for secure and appropriate data disposal to prevent unauthorized access or accidental disclosure.
7. Monitoring and Review: ISO 27001 requires organizations to establish processes for monitoring the effectiveness of information security controls, including those related to data assets. This includes conducting regular reviews, audits, and assessments to ensure that the implemented controls are operating effectively, and identifying any areas for improvement or potential vulnerabilities.
8. Continuous Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continuous improvement in information security management. Organizations are expected to regularly review and update their data asset management practices based on changes in technology, business requirements, and the evolving threat landscape. This ensures that data assets are adequately protected and that security measures remain up to date.
While ISO 27001 does not explicitly provide a detailed framework for “Data Asset Management” as a stand-alone concept, it addresses the management of data assets within its broader framework for information security management. By following the principles and requirements of ISO 27001, organizations can establish a systematic approach to manage and protect their data assets effectively.
Useful links for further reading:
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/blogs/
ZEBSOFT utilities
Information Security Management System (ISMS), Risk Assessment, Risk Treatment.Asset Inventory,Control Objectives,Security Policies,Incident Management,Continuous,Improvement,Certification,Access Control,Encryption,Audit and Compliance,Vulnerability Management,Data Protection,Business Continuity,Security Awareness Training,Information Classification,Security Metrics,Supplier Security,Physical Security
Zebra Software Limited
- Head office: Booths Hall, Booths Park, Knutsford, Cheshire, WA16 8GS.
- Registered office: Riverside, Mountbatten Way, Congleton CW12 1DY, United Kingdom
- Registered in England and Wales 11901161
- ICO number A8778081
Corporate
Audit Management, Streamlined Processes, Centralized Data Management, Automated Reminders, Real-time Insights, Data Security, Efficiency in Audits, Effective Audits, Hassle-free Audits, Business Growth, Innovative Audit Solutions, ZEBSOFT Platform, Audit Excellence, Organizational Excellence, Scalable Audit Solutions, Audit Workflow Automation, Simplified Audits, Secure Audit Data, Audit Optimization, Enhanced Decision-Making

