ISO 14001 Environmental Management System Software
Control environmental compliance with an ISO 14001 Environmental Management Software system that will manage all your requirements and controls in one platform creating continual improvement of you environmental controls. Cloud Based EMS Software control for multiple sites & rapid deployment. A standalone or combined environmental management system, for ISO Management. Built on ISO structures.
Certification / Accreditation for ISO14001 Environmental Management: Fully templated system, Consultancy services, Implementation, Certification, Training
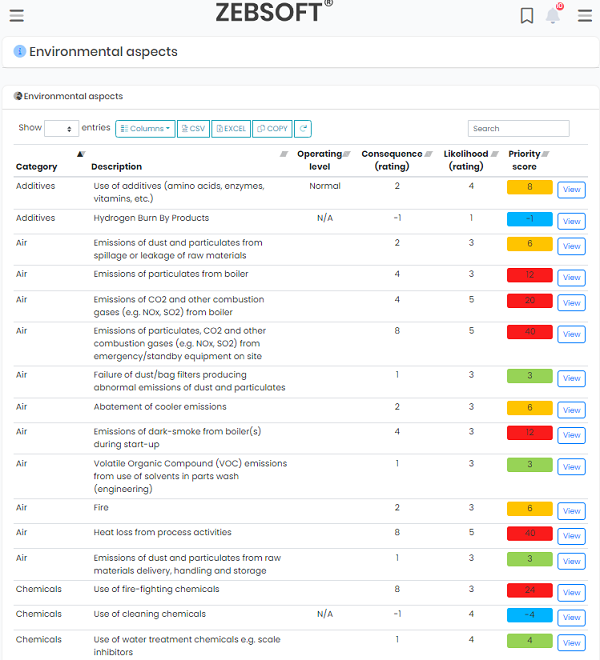
Environmental Aspects and Impacts:
Manage Environmental risks and benefits by creating visibility and understanding of your environmental factors.
- Align your environmental management to your organisational processes.
- Our environmental management software will communicate the importance of environmental awareness maintaining ownership.
- Through the publication of accurate aspects and impacts information users are informed and understand their responsibility toward maintaining environmental controls.
- Enable a culture of environmental responsibility, by motivating people to participate & support the environmental risk management function.
- Improve environmental strategies and controls by managing process and operational ongoing risk.
- Add risk modules for Quality, Health & Safety, Information Security & Contingency planning
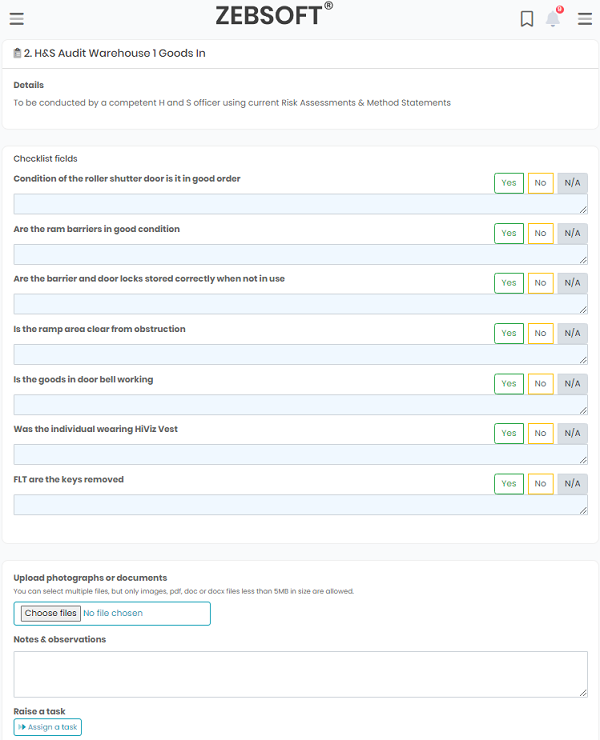
Efficient and accurate environmental checks:
Quick Check & Pro Check – Checklist audits for day to day control
- Audits are created to predetermined criteria
- Have visibility of the process and interdependencies during the audit.
- Persons carrying out the audit have no influence on the result due to background scoring methods.
- Add photos and evidential documents to the audit report in real time.
- Escalate to Incident & Non-Conformity management real time.
- Report results instantaneously with senior management alerts.
Control multiple sites:
Allocate system resource to given sites, controlled of communicated information, visibility & ownership of process.
- Cloud based access via private and secure AWS (London UK) servers
- Control GRC communication from within the platform removing cross platform errors.
- Allocate specific process and general tasks with expected completion times.
- Quality management software system documents are controlled & authorised centrally, no local level documentation to control.
- Have evidence of communication with document signing.
- System alerts generated through email and notifications

Control of documented environmental information:
Misuse of documentation becomes a thing of the past, communicate documents with classified access & user signing.
- Strict ISO & GRC document control, embodying the principles of ISO27001 & ISO9001.
- Complete control over your documents, creation, indexing & publishing, controlled to a high degree.
- Increase profitability at business and process level through the control exercised over documents.
- Private secure AWS (London UK) document storage environment for your documents.
- Full digitisation, the system controls documentation only the authorised version will be in use.
- Gain control over integrity, security, classification, distribution, reproduction.


Environmental Control Mechanisms:
Define your organisations Roles, Responsibilities and Authorities. Create understanding of where the lines are drawn with clarity for all.
- Create the structures set by ISO9001 for organisational management.
- Have visibility of the functions required for; planning, organising, evaluating, staffing & leading.
- Maintain disciplines via an incredibly strong communication platform that removes the possibility of oversight.
- Use the principles of consistent & continual improvement as a default.
- Give management the tool they need to bring about real improvement through control.
- Retain a complete and evidential data trail of actions.

ISO14001 Environmental Management System (EMS)
Zebra Software Limited
- Head office: Booths Hall, Booths Park, Knutsford, Cheshire, WA16 8GS.
- Registered office: Riverside, Mountbatten Way, Congleton CW12 1DY, United Kingdom
- Registered in England and Wales 11901161
- ICO number A8778081
Corporate

